Server 2008 vs. Server 2012 vs. CentOS NAS PerformanceAll modern operating systems provide built-in network-attached storage (NAS) capabilities allowing one to share files between users and different devices, backup data and stream rich media content. Different operating systems provide different NAS capabilities, use different file systems and therefore the performance of a NAS device greatly depends on the used operating system. The purpose of this review is to compare the performance of NAS capabilities in the following operating systems:
In order to test the performance of NAS capabilities in mentioned operating systems, we have used 4 identical virtual machines with each one configured to use 4 CPU cores, 4 GB of system memory and installed on the same 8-core physical server with 32 GB of system memory running the Windows Server 2008 R2 (64-Bit) host operating system. Host Server Configuration:
Guest Virtual Machines Configuration:
An identical set of tests with an identical set of files has been performed on each operating system and before each test the virtual machine has been restarted. All tests were performed using DiskBoss v4.7.28, which is capable of analyzing disk space usage, classifying files, searching duplicate files, synchronizing files, copying files and deleting files using a number of parallel threads. Each operating system has been tested using an identical set of benchmarks including:
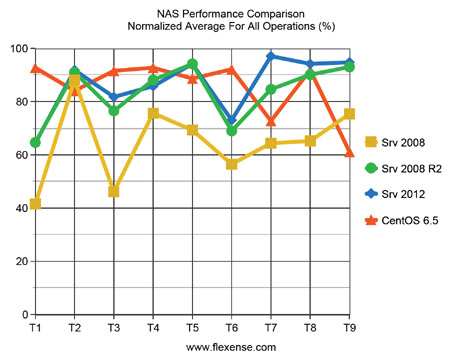
Average NAS performance results from all tested operating systems were normalized and compared relative to the maximum performance for each specific test. 
According to the normalized NAS performance results, which show a normalized average NAS performance for all types of benchmarks for each operating system, the Windows Server 2012 delivers a slim 1% performance improvement over the CentOS Linux v6.5 and a 3% improvement over the Windows Server 2008 R2 while the Windows Server 2008 delivers approximately 20% slower NAS performance results compared to other operating system. 
For users required to write a large number of small files to a NAS storage device, the CentOS Linux v6.5 is a clear winner with up to 30% improvements over the Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows Server 2012 while the Windows Server 2008 delivers significantly slower results. 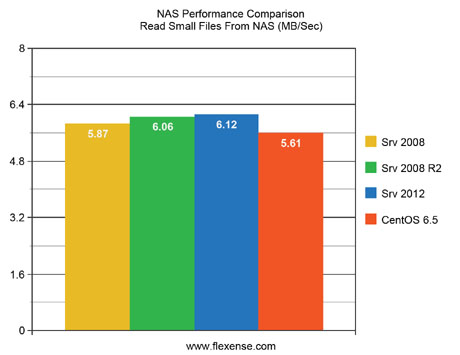
For users required to read a large number of small files from a NAS storage device, the Windows Server 2012 delivers the best results with the Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Serer 2008 and CentOS Linux v6.5 following with a minor performance degradation. 
For users required to write medium-sized files to a NAS storage device, the CentOS Linux v6.5 delivers the best results followed by the Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2008 R2 with an approximate 10% performance degradation while the Windows Server 2008 delivers significantly slower performance results. 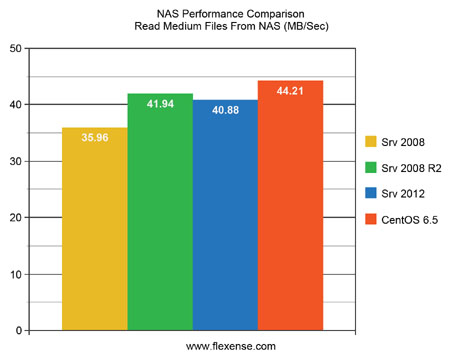
When reading medium-sized files from a NAS storage device, the CentOS Linux v6.5 delivers the best results followed by the Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows Server 2012 with a slim performance degradation while the Windows Server 2008 delivers significantly slower performance results. 
When writing a small number of large files to a NAS storage device, the situation changes and the Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2008 R2 deliver the best results followed by the CentOS Linux v6.5 with an approximate 6% performance degradation while the Windows Server 2008 delivers significantly slower performance results. 
When reading a small number of large files from a NAS storage device, the CentOS Linux v6.5 delivers more than 20% of performance improvements compared to other operating systems making it a clear winner for these specific operations. 
For disk space analysis and file classification operations, which mostly require to read directory structures from a NAS storage device, the Windows Server 2012 delivers significantly higher performance results with up to 8,000 files/sec of disk space analysis speed followed by the Windows Server 2008 R2 with up to 7,000 files/sec of disk space analysis speed. The CentOS Linux v6.5 and the Windows Server 2008 deliver significantly slower results with up to 6,000 files/sec and 5,300 files/sec of disk space analysis speed respectively. 
For duplicate files search operations, which require a large number of random read operations, the Windows Server 2012 delivers the best NAS performance results closely followed by the CentOS Linux v6.5 and Windows Server 2008 R2 while the Windows Server 2008 delivers significantly slower performance results. 
For file delete operations, the Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2008 R2 deliver the best results followed by the Windows Server 2008 with a 20% performance degradation while the CentOS Linux v6.5 delivers significantly slower performance results. Conclusions:
* This performance review has been prepared for information purposes only and we strongly advise you to make your own performance evaluations using your specific hardware components and datasets. |